
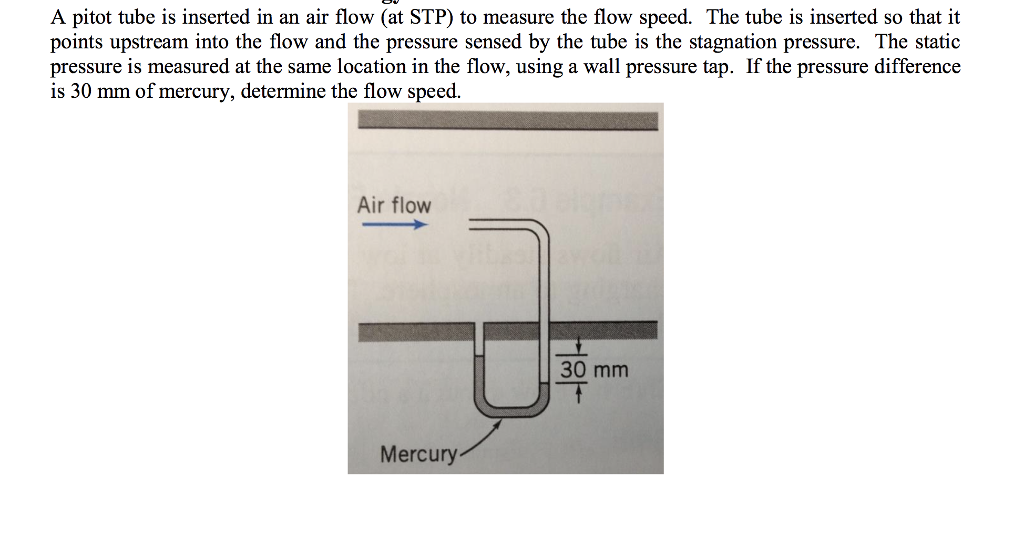
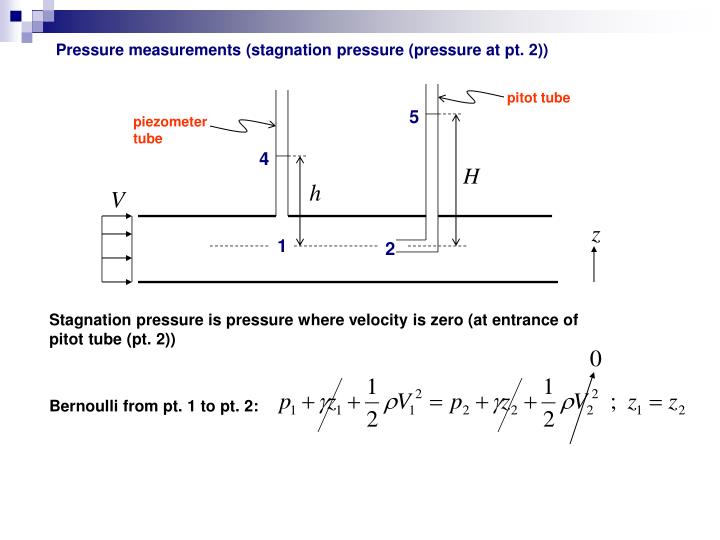
This system involves placing a pitot tube inside another tube with static ports. The static pressure is used in all measurements, while the pitot pressure is used only to determine airspeed. It works by measuring pressures or pressure differences and using these values to assess the speed and altitude. Where is the static pressure of fluid in the pipe, and are the densities of the fluid in the pipe and manometer fluid, is specific gravity of fluid in the pipe, is the gravitational constant, and is the difference in height of the manometer fluid. The pitot-static tube has two openings, one in the front and one along the sides, used to measure air, gas or liquid flow. The pitot-static system of instruments uses the principle of air pressure gradient. The pitot-static tube is mounted on the aircraft, or in a wind tunnel, so that the center tube is always pointed in the direction of the flow and the outside holes are perpendicular to the. If the readout continues to oscillate increase the damping (DAMP). Wait for the readout on the display to stabilize. Ensure that the Pitot Static tube is aligned with the axis of the duct using the alignment guide on the tube as a reference.
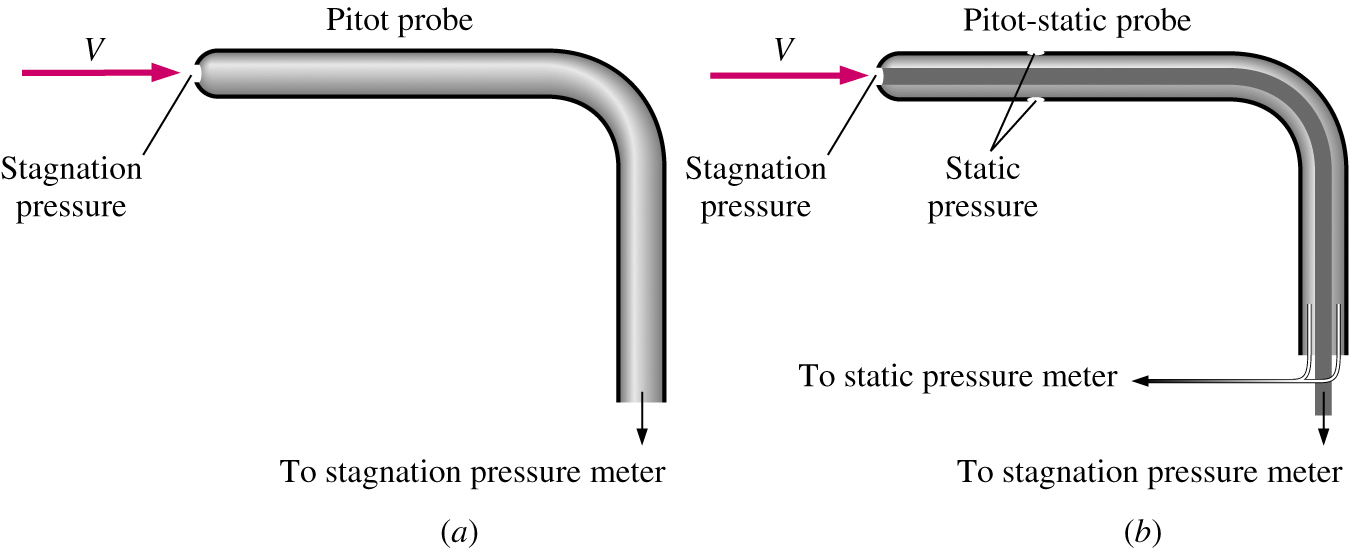
This equation can be rearranged and used to solve for fluid velocity or difference in height of the fluids in the manometer: The transducer measures the difference in pressure in the two groups of tubes by measuring the strain in a thin element using an electronic strain gauge. Carefully insert the Pitot Static tube into the duct and position at the first traverse location. The equation for the difference in pressure in a manometer is substituted into the simplified Bernoulli equation: Thus we obtain the simplified form of Bernoulli's equation: In a pitot-static tube, we have two different pressure, the static pressure p s and the total pressure p 0 p s + 1 2 v 2, which comes from the Beroulli equation for incompressible flows. The two points that are being evaluated are at the same height, so and drop out. The difference in pressure (pR pT), shown as h in the manometer of Figure 49. The stagnation pressure head is 6 m and static pressure. A Pitot-static tube is a device for measuring the velocity of moving fluids or of the velocity of bodies moving through fluids. All terms on the right side refer to point 2, a point upstream from the pitot tube. Static Pressure is conveniently measured by drilling a hole in the wall or the pipe, called the Pressure Tap (Fig. The Questions and Answers of A pitot-static tube is used to measure the velocity of water in a pipe. Bernoulli's equation is used to calculate the velocity of the bulk fluid in the pipe by using this pressure difference in the pitot tube:Īll terms on the left side represent the stagnation point (entrance of the pitot tube) here is the stagnation pressure and is the velocity of fluid in the pipe at point 1. Pitot tubes are used to measure the velocity of a fluid moving through a pipe by taking advantage of the fact that the velocity at the height of the bend in the tube (stagnation point) is zero. The pressure inside the pitot tube increases on the cost of kinetic head loss. Some kinetic energy density of the fluid flowing through the pipe is converted into pressure, resulting in a change in manometer height. Stagnation Pressure is the pressure which is achieved when a flowing fluid is reduced to zero velocity in a frictionless process or say it’s the pressure at the stagnation point in a fluid flow. If the air on one side of the diaphragm is at the static pressure, and. The magnitude of stagnation pressure can be derived from Bernoulli equation For incompressible flow and no height changes. Routine for calculating the velocity from //a pitot tube and MPXV7002DP pressure differential sensor float V_0 = 5.0 // supply voltage to the pressure sensor float rho = 1.Pitot tubes are used to measure the velocity of a fluid moving through a pipe by taking advantage of the fact that the velocity at the height of the bend in the tube (stagnation point) is zero. The dynamic pressure is then determined using a diaphragm inside an enclosed container.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
